Select the Correct Detailed Mechanism for the Following Reaction.
Demonstrate your knowledge of Grignard reactions by suggesting a plausible sequence. Memorize Reaction Orientation where Appropriate Stereochemistry where Appropriate and Mechanism where Appropriate.
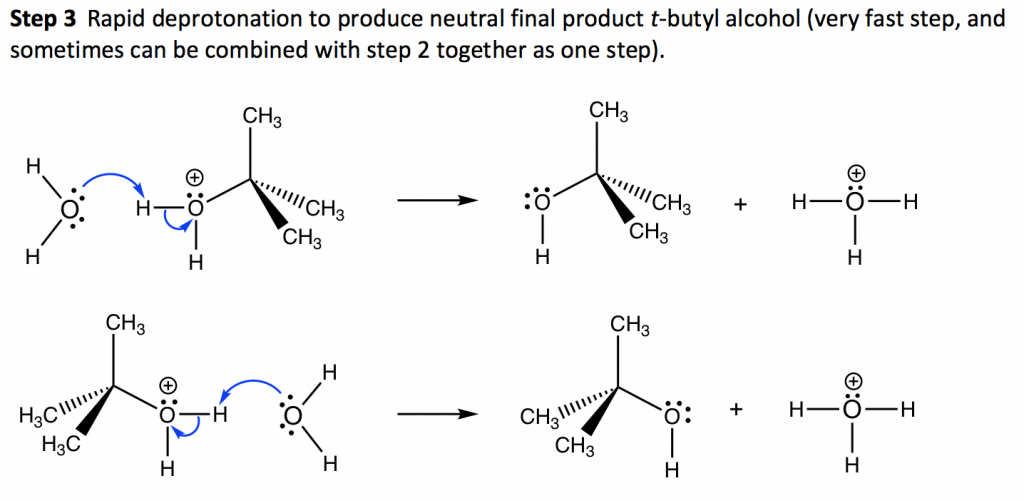
7 4 Sn1 Reaction Mechanism Energy Diagram And Stereochemistry Organic Chemistry I
The products are higher in energy than the reactants.

. 1 2 NO 2 NO 3 NO. Click again to see term. Write the equation for the overall reaction from the mechanism above.
23-dimethylcyclohexanol H 2 SO 4 A B C D E Page 9 13. A reaction mechanism is a hypothesis. Predict the MAJOR product of the following reaction.
A A ---- C E slow Step 2. 12 pts For each of the reactions below fill in the empty box corresponding to product. The following mechanism for the reaction between H2 and CO to form formaldehyde H2CO has been proposed.
2 NO 3 NO O 2. The observed rate dependence is found to be one-half order in 1-12 and first order in O. If the experimental data do not agree then the proposed mechanism is wrong.
NO2g COg NOg CO2g NO 2 g CO g NO g CO 2 g Figure 1. Slow NO2 NO2- NO3 NO fast NO3 CO - CO2 NO2 A. 2 NO 2 NO 3 NO NO 3 NO O 2.
For an example of a mechanism consider the decomposition of nitrogen dioxide into nitric oxide and oxygen. That means that mechanism 2 is possible. E B ---- A D fast Overall reaction.
One example is the reaction of nitrogen dioxide with carbon monoxide. It only shows that the chosen mechanism works perfectly for this reaction. Even if one or more fast steps occur in a reaction the overall reaction cannot proceed any faster than the slowest step.
Predict the MAJOR product of the following reaction. AB B -- AB2 slow and the rate kABB. The entropy change in the reaction will probably have little effect on the free energy change.
2 NO 2 g 2 NO g O 2 g The mechanism of this reaction is believed to involve the following two elementary steps. The net balanced equation is. LatextextCl_2gleftrightharpoons2textClglatex fast k 1 represents the forward rate constant k 1 the reverse rate.
The following reaction mechanism has been proposed for a reaction. For reactions that you expect to yield multiple products draw one major product. Give only one answer in each box.
Some chemical reactions have mechanisms that consist of a single bimolecular elementary reaction. Fast equilibrium slow fast 1-12 H co 1-12C0 a k 47 Write the balanced equation for the overall reaction. The net balanced equation is.
The reaction of CO with Cl 2 gives phosgene COCl 2 a nerve gas that was used in World War I. For reactions that yield multiple enantiomers draw only one enantiomer in the box and include the note enantiomer. Step1Step2X2YZ2X2YZ2 slowX2YZ2X2YZZ fast.
Note that the intermediate species NO 3 has only a transient existence and does not appear in the net equation. That the mechanism is proven to be correct. The following list of suggested reagents is sufficient to accomplish all necessary reactions but you.
Rate kAB kA2 rate k A B k A 2. Consider the following representation of a reaction mechanism. A mechanism must satisfy the following two requirements.
A B ---- C D. This type of substance is often used up and regenerated. A reaction mechanism can be used to predict the exponents in the rate law which may be compared to the measured results from experimental data.
Make sure you draw the correct structure for each intemediate product and clearly indicate the reagents required for each reaction. The reaction is endothermic. BWrite the rate law for the.
The bonds formed in the products are stronger than the bonds in the starting materials. A ______ is a substance that increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed. A reaction mechanism describes a series of single reaction steps that sum to the overall chemical equation.
Select a possible mechanism for the reaction. Use the mechanism shown here to complete the following exercises. The reaction favors the products at equilibrium.
Tap again to see term. Draw a detailed curved arrow mechanism that leads to the major product. Remember that in simple cases where the slow step is the first step of the mechanism the orders tell you what is taking part in the slow step.
NH NO2 Br H3C Cl NO2 Br H2NCH3 NO 2 Br H3CNCl HH N Br H3CNHCl-H NO2 Br H3CNHCl NO2 Br H3CNHCl NO2 Br O. Consider the following three-step representation of a reaction mechanism and rate laws. A B -- AB fast and the rate kAB Step 2.
Orientation Stereo Mechanism 1 HrB r no peroxides c. Summary of Alkene Reactions Ch. In this case the reaction is first order with respect to both A and B so one molecule of each must be taking part in the slow step.
Reaction Mechanisms act as tools to do this by allowing. Select all that apply. Which one of the following types of reaction mechanism is not involved in the above sequence.
It gives a prediction of the rate law that can be compared to experimental data to confirm or refute the proposed mechanism. 6 10 points Identify the products of the following reactions. This is a reasonable proposal.
2 NO 2g 2 NO g O 2g The mechanism of this reaction is believed to involve the following two elementary steps. Cl NO2 Br CH3NH2 Product. -all are drawn using 1-methylcyclohexene as a prototype alkene because both orientation and stereochemistry effects are readily apparent.
Which of the following is a correct mechanism for the formation of 2-methylbut-2-ene from 2-bromo-3-methylbutane. Clearly indicate resonance structures and charges in the intermediates a Mechanism.
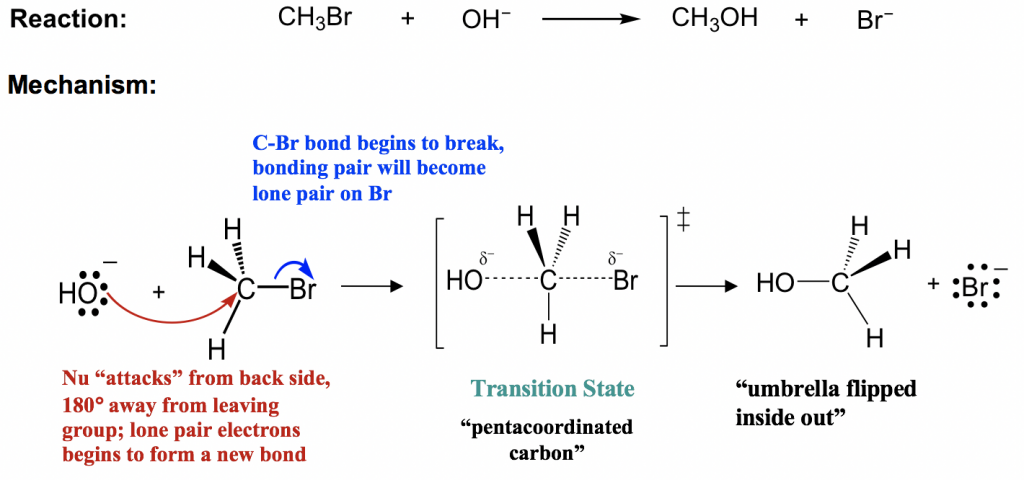
7 2 Sn2 Reaction Mechanism Energy Diagram And Stereochemistry Organic Chemistry I
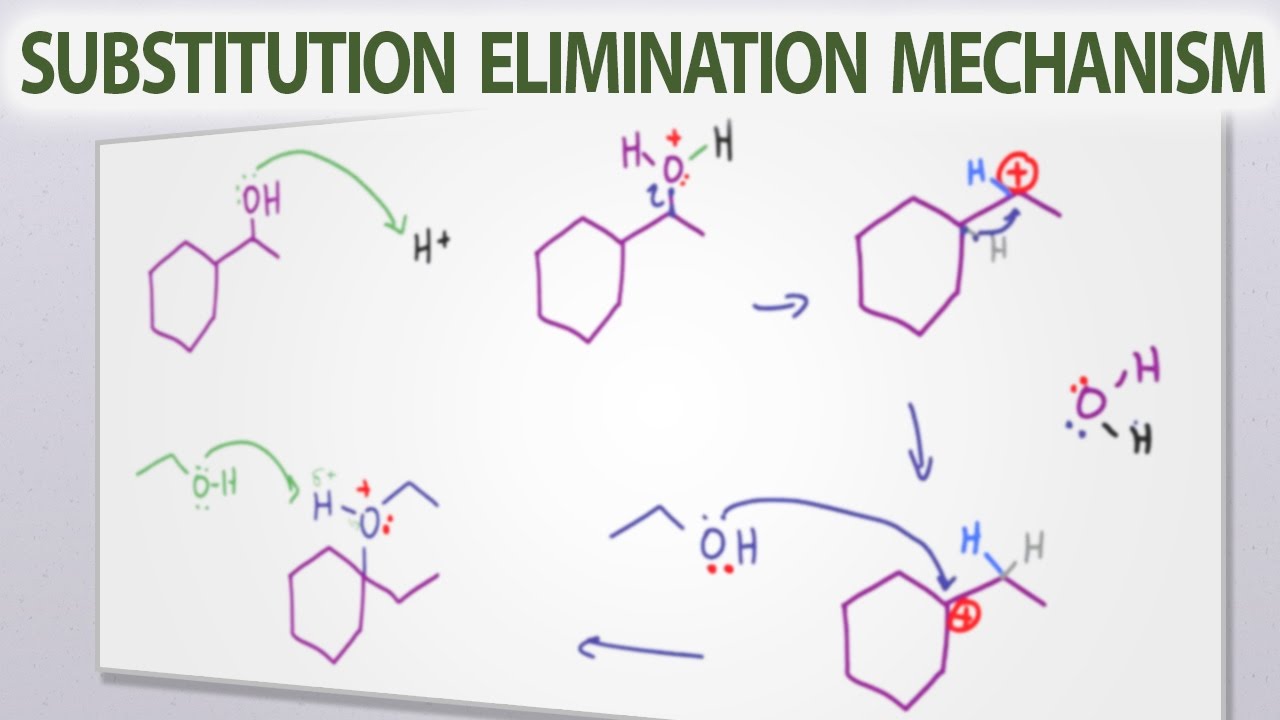
Choosing Sn1 Sn2 E1 E2 Reaction Mechanism Given Reactant And Product Orgo Sn1 Sn2 Organic Chemistry Study Teaching Chemistry Organic Chemistry

Determine Whether Each Of The Following Reactions Proceeds Via An Sn1 Or Sn2 Mechanism Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic Synthesis
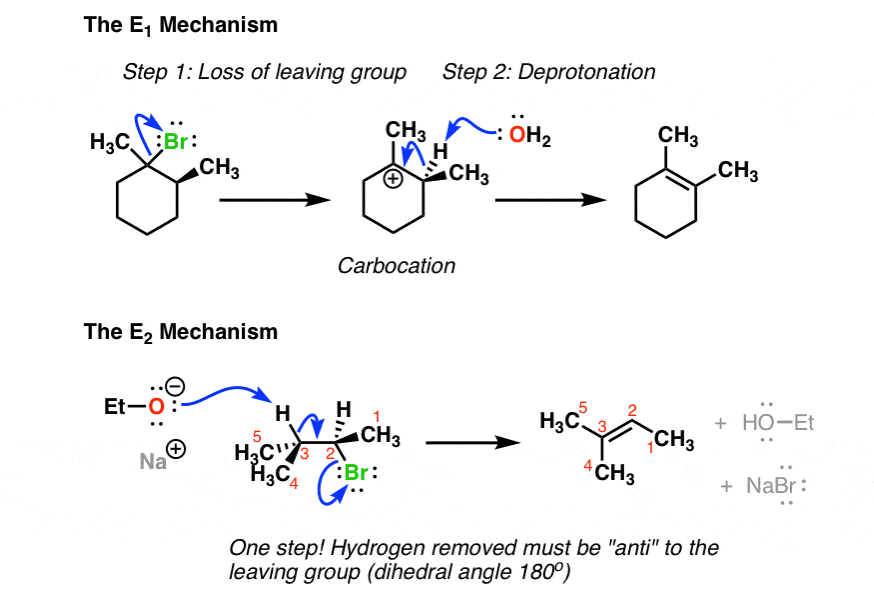
E1 Vs E2 Comparing The E1 And E2 Reactions Master Organic Chemistry
Comments
Post a Comment